Facilities
The objective of the existing monitoring infrastructure installed in the campus is to perform a high level monitoring of the main facilities and connected energy systems with particular focus on electrical energy usage in terms of electrical loads and power generation systems.
Electrical loads
The campus is electrically fed by a loop of ten medium voltage transformer substations, which provide low voltage electrical power to the distribution system and utilities. This electrical configuration allows to reduce electrical losses thus improving medium to low voltage conversion efficiency. Each substation provides electricity to a given area of the campus and is identified through a letter, as shown in the following figure.
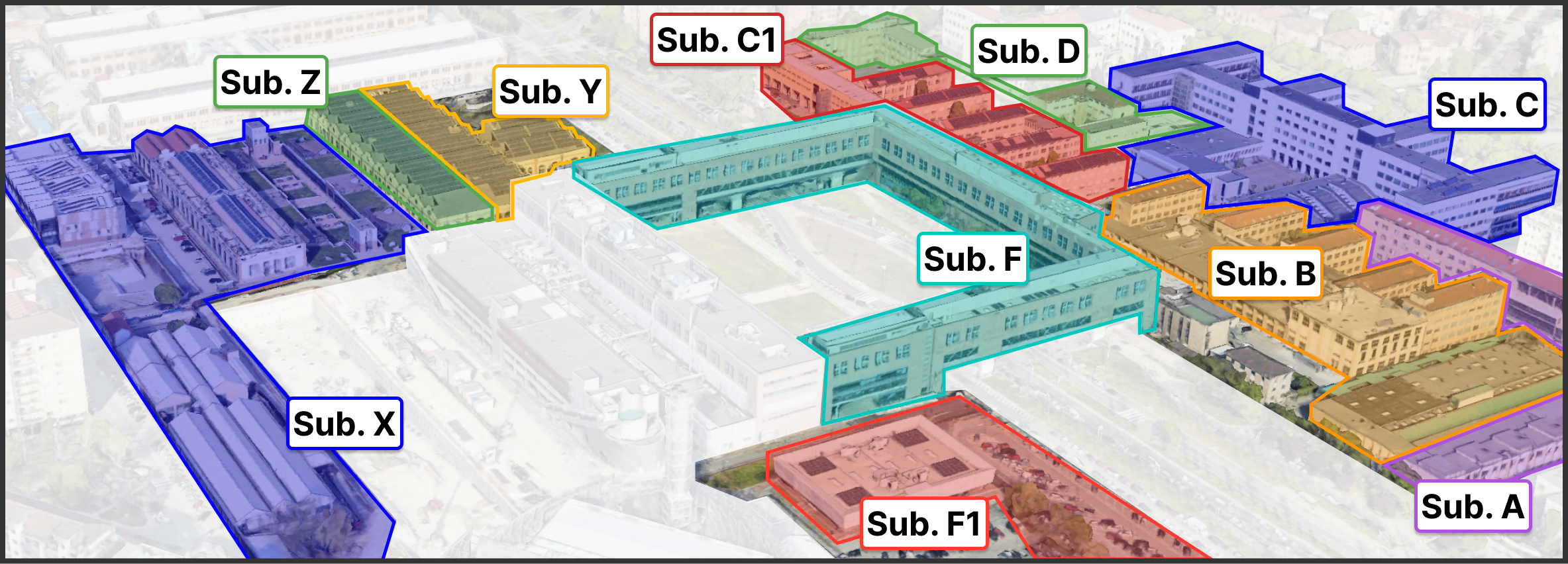
Each substation electrically feeds several kind of electrical loads such as laboratory facilities, classrooms, commercial activities, lighting equipment and energy systems like chillers and HVAC systems. Thanks to a pervasive sub load monitoring of such systems, it is possible to disaggregate the total electrical load by identifying the share of the different loads with a satisfying level of detail.
Power generation systems
To meet the increasing electricity demand that the campus experienced during the years, it has been equipped with seven PV systems, each of them located in a different building of the campus, consisting in more than 3000 PV modules and 43 inverters. In 2023 the total installed capacity almost reached 1 MW with an annual average production of about 1.3 GWh.
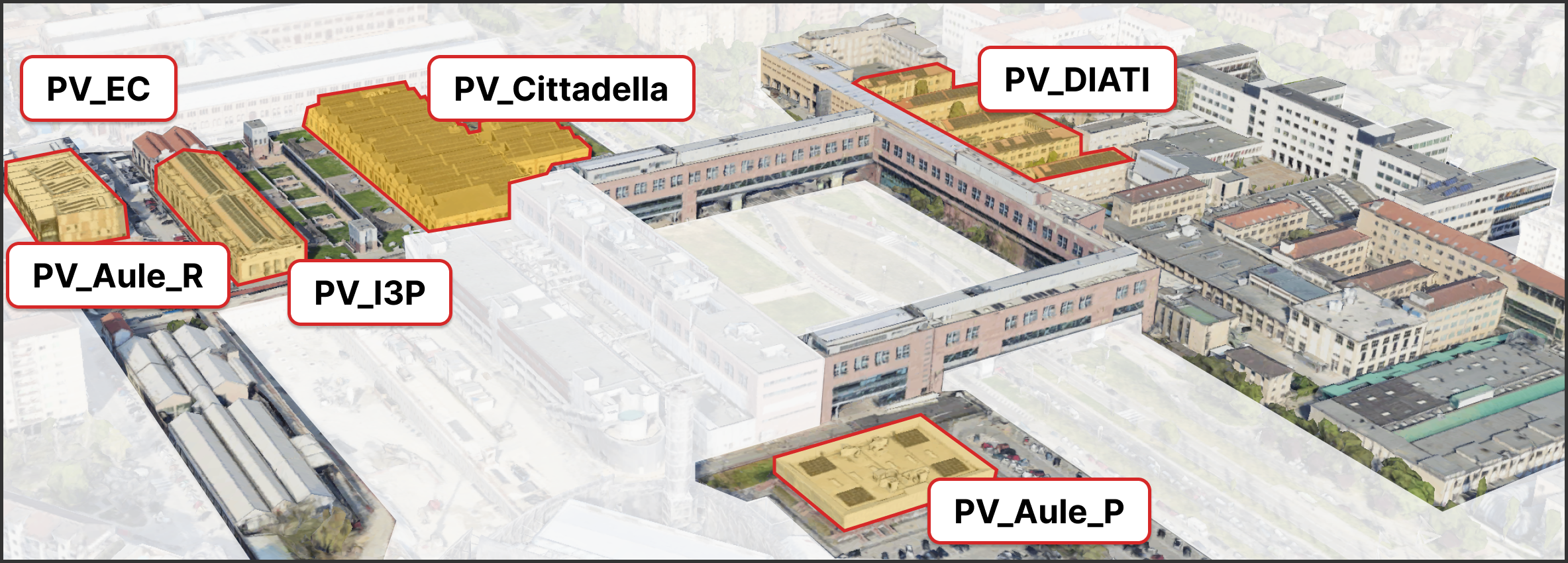
The installation of these PV systems took place at various times, with each system varying in peak power, array configuration, and associated monitoring infrastructure as summarized in the table below.
| Name | Year | Power | # Modules | Module Rating | # Inverters | Sensors | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PV_Cittadella | 2015 | 604 kWp | 1849 | 327 W | 27 | Power, Temp., Irradiance | Main switch AC metering |
| PV_DIATI | 2019 | 183 kWp | 487 | 360 W | 8 | Power | Main switch AC metering |
| PV_Aule_P | 2018 | 50 kWp | 144 | 345 W | 2 | Power | AC side of switchboard |
| PV_Aule_R | 2021 | 47 kWp | 117 | 400 W | 3 | Power | AC side metering |
| PV_EC | 2016 | 47 kWp | 154 | 305 W | 4 | 4x Power (inverter level) | Modules on facade, roof, and transparent facade |
| PV_I3P | 2009 | 31 kWp | 140 | 220 W | 2 | Power, Temp., Irradiance | Structural glass modules with Argon chamber |
Weather station
The campus hosts a weather station located on the rooftop of the main campus building, as shown in the Figurebelow. The primary sensors include a barometer for atmospheric pressure, an anemometer to measure the wind speed and direction, a thermohygrometer for air temperature and relative humidity, and a rain gauge to measure the amount of precipitation and intensity. Additionally, the station is equipped with solar radiation sensors: a pyrheliometer, which — using a sun tracker — measures direct normal and horizontal solar irradiance, and a pyranometer to measure global solar radiation (including direct, diffuse, and reflected radiation). Such sensors are regularly maintained and calibrated if necessary.
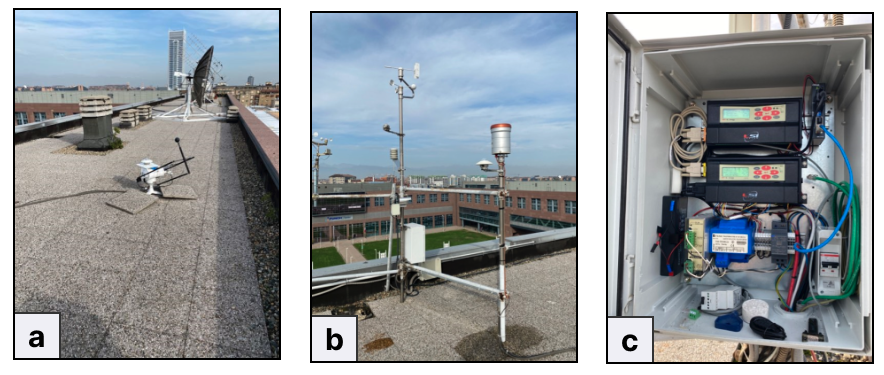
The data acquisition and transmission is ensured by a wired communication through a data logger for environmental applications, which due to its low consumption, the range of signals it is able to receive, its protection against difficult environmental conditions, it is particular suitable to carry out measures in meteorological and hydrologic applications, air quality, internal and external environmental monitoring.